If you are wondering what does a financial analyst do, you are not alone. The role of a financial analyst is one of the most crucial in the finance and business sectors. Whether you are a student exploring career options, a fresh graduate looking for your first finance job, or someone aiming to switch careers, understanding the responsibilities, skills, and career scope of a financial analyst is essential. In this guide, we will comprehensively cover what a financial analyst does, their roles, responsibilities, required skills, career progression, and much more. Moreover, by the end of this blog, you will gain complete clarity about how to build a successful career in financial analysis.
Table of Contents
ToggleWho is a Financial Analyst?
A financial analyst is a professional who evaluates financial data, prepares reports, and makes recommendations to help businesses, investors, and organizations make informed financial decisions. In simple terms, a financial analyst analyzes money matters to ensure that companies can optimize investments, minimize risks, and maximize profits.
Financial analysts are indispensable in sectors like banking, investment, corporate finance, stock markets, and asset management. They act as the bridge between raw financial data and strategic decision-making.
Key Point: Why Financial Analysts are Important
Financial analysts play a critical role in helping businesses understand trends, forecast future performance, and make investment decisions. Without their insights, organizations could face risks due to poor financial decisions, missed investment opportunities, or inefficient allocation of resources.
In essence, knowing what does a financial analyst do is vital for students and professionals aiming for a career in finance, as it helps in identifying the right skills, qualifications, and growth opportunities.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Financial Analyst
Understanding the roles and responsibilities of a financial analyst is the first step toward building a successful career in this field. Their duties vary depending on the organization, sector, and specific role, but the core responsibilities typically include:
1. Financial Data Analysis
Financial analysts examine financial statements, balance sheets, profit and loss accounts, and cash flow statements. Their goal is to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that could impact business performance.
2. Preparing Financial Reports
They prepare detailed financial reports and presentations that summarize findings, predictions, and recommendations. These reports are used by managers, investors, and executives for strategic decision-making.
3. Forecasting and Budgeting
One of the most important tasks is financial forecasting. Financial analysts predict revenue, expenses, and investment returns, helping companies plan budgets efficiently. This ensures that resources are allocated optimally.
4. Investment Analysis
Financial analysts evaluate potential investment opportunities, assess risks, and determine the expected return on investment (ROI). This is especially critical in banking, portfolio management, and investment firms.
5. Risk Management
By analyzing market trends, economic conditions, and financial reports, financial analysts help organizations identify financial risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
6. Supporting Strategic Decisions
A financial analyst provides actionable insights that support long-term business decisions, including mergers, acquisitions, expansions, and cost-cutting strategies.
7. Monitoring Market Trends
Financial analysts continuously monitor the economy, market trends, and competitor performance. This enables companies to adapt their strategies proactively rather than reactively.
Types of Financial Analysts
Financial analysts are not a one-size-fits-all role. Depending on your interests and skills, you can specialize in different types of financial analysis. Here are the main types:
1. Investment Analyst
Investment analysts focus on evaluating stocks, bonds, and other securities to provide investment recommendations for clients or organizations.

Deepak Goyal CFA & FRM
Founder & CEO of RBei Classes
- 16,000+ Students Trained in CFA, FRM, Investment Banking & Financial Modelling
- 95% Students Successfully Placed • 94.6% Pass Rate In Exam
2. Credit Analyst
Credit analysts assess the creditworthiness of individuals or organizations to determine loan eligibility and minimize financial risk.
3. Budget Analyst
Budget analysts work with organizations to develop, review, and manage budgets, ensuring financial efficiency and compliance.
4. Risk Analyst
Risk analysts focus on identifying financial risks and implementing strategies to mitigate potential losses in investment or business operations.
5. Corporate Financial Analyst
Corporate financial analysts work internally within companies, helping senior management with strategic planning, financial modeling, and internal financial reporting.
6. Quantitative Analyst (Quant)
Quants use mathematical and statistical models to analyze financial data and develop complex trading strategies, often in investment banks or hedge funds.
Skills Required to Become a Financial Analyst
If you are aiming to understand what does a financial analyst do, it’s equally important to know the essential skills required for this career.
1. Analytical Skills
Analytical skills are the backbone of a financial analyst’s role. You must be able to interpret data, identify trends, and make logical conclusions.
2. Attention to Detail
Even a small error in financial analysis can lead to incorrect recommendations. Precision and accuracy are crucial in this profession.
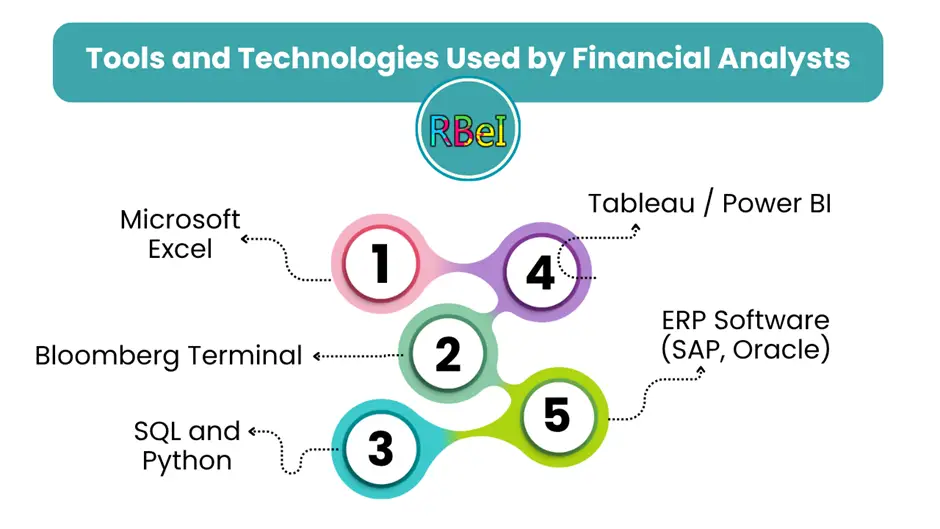
3. Technical Skills
Financial analysts often use software like Excel, SQL, Python, R, and financial modeling tools. Knowledge of financial databases like Bloomberg or Thomson Reuters is highly valuable.
4. Communication Skills
It’s not enough to analyze data. Financial analysts must effectively communicate findings to non-finance stakeholders through reports, charts, and presentations.
5. Problem-Solving Ability
Financial analysts must identify problems, develop solutions, and provide actionable insights for decision-making.
6. Knowledge of Finance and Economics
A strong understanding of accounting principles, corporate finance, investment analysis, and macroeconomic trends is essential.
7. Critical Thinking
Financial analysts must challenge assumptions, anticipate risks, and think strategically to provide high-quality advice
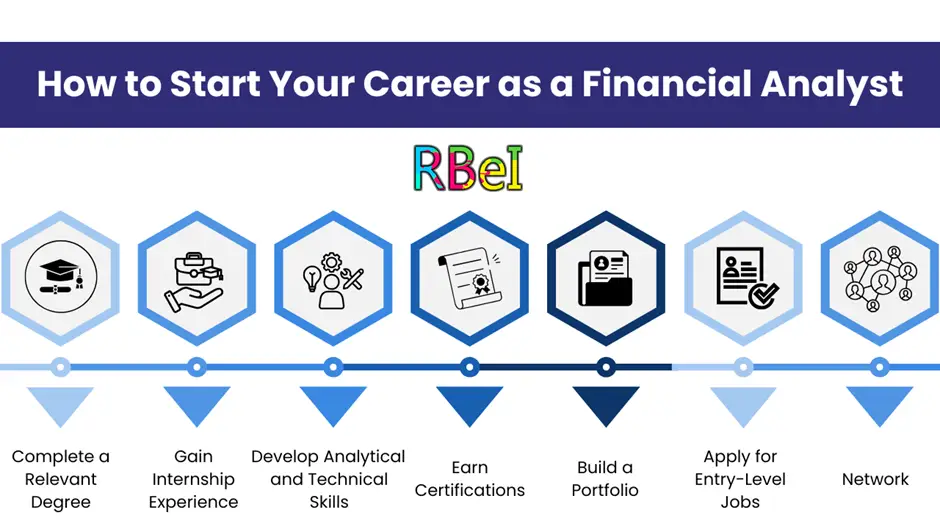
Educational Qualification and Career Path
Knowing the educational requirements and career path is vital for students and professionals planning to become financial analysts.
Educational Requirements
- Bachelor’s Degree: A degree in finance, economics, accounting, business administration, or mathematics is usually required.
- Certifications: Certifications like CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst), FRM (Financial Risk Manager), or CPA (Certified Public Accountant) can boost career prospects.
- Master’s Degree: An MBA with a focus on finance or investment is highly beneficial for higher-level positions.
Career Path
The career progression for financial analysts usually follows this path:
- Junior Financial Analyst / Entry-Level Analyst – Focus on data analysis and reporting.
- Financial Analyst / Senior Analyst – Take on more complex projects and investment analysis.
- Finance Manager / Senior Financial Analyst – Oversee teams and manage corporate finances.
- Director of Finance / VP of Finance – Strategic leadership role, managing large-scale financial operations.
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO) – Executive-level role responsible for overall financial strategy and management.
Career Scope and Opportunities
The career scope of a financial analyst is vast and promising. Demand for skilled analysts is increasing across industries.
1. Banking and Investment Firms
Financial analysts are in high demand in investment banking, commercial banking, and asset management.
Must Read: Investment Banking Course India
2. Corporate Sector
Companies across all industries hire financial analysts to optimize finances, plan budgets, and manage investments.
3. Consulting Firms
Consulting firms hire financial analysts to advise clients on financial strategy, risk management, and investment decisions.
4. Government and Non-Profit Organizations
Government agencies and non-profits need financial analysts for budgeting, auditing, and policy implementation.
5. Entrepreneurship and Startups
Startups require financial analysts to manage finances, secure funding, and ensure business growth.
Salary Prospects
| Experience Level | Salary Range (India) |
|---|---|
| Entry-Level | ₹3 – ₹5 LPA |
| Mid-Level | ₹6 – ₹12 LPA |
| Senior-Level | ₹15 – ₹30 LPA+ |
| CFO / Executive Level | ₹50 LPA+ |
Challenges Faced by Financial Analysts
Even though the role is rewarding, financial analysts face certain challenges:
- High Pressure: Decisions affect business outcomes and investments.
- Constant Learning: Markets, technologies, and regulations change rapidly.
- Long Hours: Especially during reporting periods or market volatility.
- Complex Data: Analyzing large datasets can be challenging.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what does a financial analyst do is essential for anyone looking to make a mark in finance. From analyzing data and preparing reports to forecasting, investment analysis, and risk management, the responsibilities are vast and impactful. Financial analysts are in demand across sectors, and the career offers excellent growth opportunities with competitive salaries.
By acquiring the right education, technical skills, and certifications, coupled with practical experience, anyone can build a successful career in financial analysis. Whether your goal is to become a senior corporate analyst, investment banker, or CFO, the opportunities are immense for those willing to put in the effort.
Key Takeaway: A financial analyst is more than just a numbers person—they are strategic decision-makers who guide organizations toward financial success. Understanding their roles, responsibilities, and career scope will help you plan effectively and achieve your professional goals.






