Volatility, stock picking, winners, risk management, and strategy – if you want to know how to pick winning stocks in a volatile market, you need more than guesswork. In this blog we will explore strategies, tools, psychology, and real tips so that you can make informed decisions even when the markets swing wildly. Even though volatility often intimidates many investors, knowing how to pick winning stocks in a volatile market can turn opportunity from chaos.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey phrases like how to pick winning stocks in a volatile market and volatility will appear repeatedly, in natural ways, so that you grasp the concept deeply.
Let’s dive in step by step.
Understanding Volatility and Why It Matters
Before we talk about how to pick winning stocks in a volatile market, we must clearly define volatility, what it means for investors, and how it shapes opportunities and risks.
What is Volatility?
Volatility refers to the degree of variation in a stock’s price over time — in short, how wildly it moves up and down. When prices jump up and down sharply, we call the stock (or the market) volatile.
Technical measures of volatility include:
- Standard deviation of returns
- Bollinger Bands: when bands widen, volatility is high; narrow bands suggest low volatility
- Average True Range (ATR): measures how far price typically moves over a period
- Beta: how a stock’s movement compares to the market index (for example, the S&P 500). A beta > 1 means more volatile than market; beta < 1 means less volatile.
Volatility is not inherently bad. In fact, it is what allows gains (and losses). But volatility magnifies both opportunities and risk.

Thus, knowing how to pick winning stocks in a volatile market is less about predicting certainty and more about managing risk, identifying high-probability setups, and staying disciplined.
Volatility vs. Risk
It’s useful to separate volatility from risk. Volatility is simply fluctuation. Risk is the chance of permanent loss or being wrong in your judgment. Sometimes, high volatility can be an opportunity; sometimes it can destroy capital if unmanaged.
Core Principles for Picking Winning Stocks in Volatile Markets
To succeed at how to pick winning stocks in a volatile market, you need to anchor yourself in core principles. These are the foundation you carry with you regardless of how crazy the markets get.
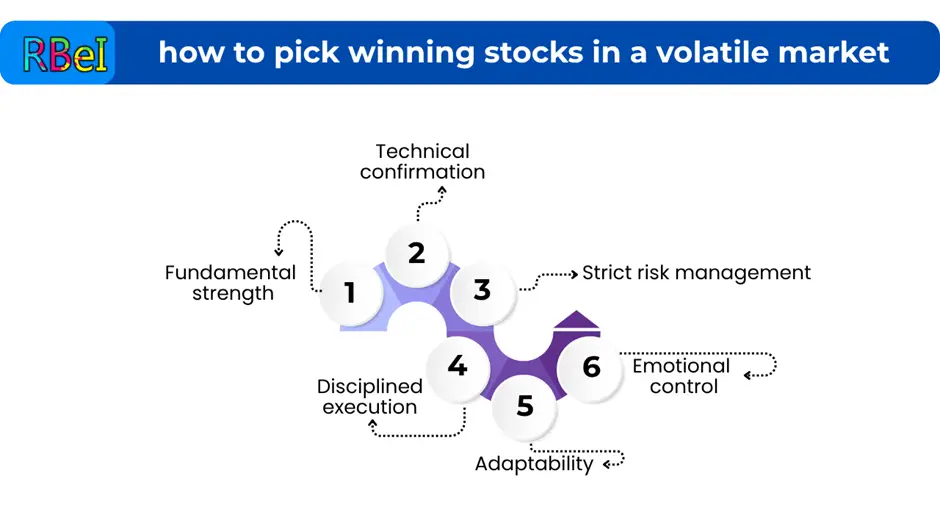
1. Start with Strong Fundamentals
Even in volatile conditions, quality tends to persist. A business with strong fundamentals (healthy revenue growth, sustainable profits, good management, manageable debt) is more likely to survive turbulence.
- Earnings consistency: look for companies that maintain profitability, even if growth slows.
- Balance sheet strength: low debt, ample cash, good liquidity.
- Competitive moat: unique advantages over rivals (brand, patent, scale, network effects).
- Management credibility and track record.
Volatility can cause even great stocks to drop, but quality gives you a better chance of recovery.
2. Use Technicals to Time Entry and Exit
Technicals become more important when volatility is high. Here are key tools:
- Breakout from consolidation: stocks that trade in a range and then break out can rally sharply in a volatile environment.
- Trend confirmation: follow the prevailing trend (up or down). Avoid betting against the trend unless strong signals reverse it.
- Resistance/support zones: identify price levels where supply or demand tends to act.
- Volume confirmation: a breakout or reversal with higher volume is more reliable.
- Volatility indicators: ATR, Bollinger Band expansions, volatility spikes.
- Moving averages: e.g., 50-day, 200-day used to gauge trend direction or dynamic support/resistance.
3. Diversification and Position Sizing (Don’t Put All Eggs in One Basket)
One of the biggest mistakes people make during volatile markets is going “all in” on a single idea. Instead:
- Limit any one stock to a small percentage of total capital (e.g. 2–5%).
- Diversify across sectors or business models.
- Use stop-loss orders or mental stops to cut losses if a trade goes wrong.
- Consider hedges (e.g. options, inverse ETFs, or protective puts) if your strategy allows.
4. Risk Management Is Non-Negotiable
When volatility is high, mistakes magnify. Thus:
- Define your maximum loss per trade before entering.
- Use trailing stops to lock in profits if the trend continues.
- Avoid emotional adjustments mid-trade; follow the plan.
- Reassess your portfolio frequently and rebalance where needed.
5. Be Contrarian When Appropriate, But Carefully
In volatile markets, crowd reactions are often exaggerated, creating mispricings:
- A contrarian investor might buy when others are panicking and sell when others are euphoric.
- But being contrarian doesn’t mean being reckless. Confirm your thesis with data, fundamentals, and conviction.
6. Use a Blend of Short-Term and Medium-Term Approaches
Depending on your time horizon:
- For shorter-term trades (days to weeks), volatility gives you more moves to ride.
- For longer-term investments, use dips to accumulate quality stocks or average your entry (e.g. dollar-cost averaging).
7. Maintain Emotional Discipline and Stay Informed
- Avoid panic selling. Markets often overreact downward first, then recover.
- Maintain a checklist or system to guard against emotional decisions.
- Stay updated on macroeconomic trends, earnings, policy, and news that drive volatility.
Step-by-Step Framework: How to Pick Winning Stocks in a Volatile Market
Now let’s lay out a sequential, actionable roadmap you (or any student) can follow to pick winning stocks during turbulent times.
Step 1: Screen for Volatility + Quality
Your first filter should combine volatility and fundamental safety.

Deepak Goyal CFA & FRM
Founder & CEO of RBei Classes
- 16,000+ Students Trained in CFA, FRM, Investment Banking & Financial Modelling
- 95% Students Successfully Placed • 94.6% Pass Rate In Exam
- Use a stock screener to filter for high beta or high historical volatility (e.g. standard deviation, ATR).
- Among those, find those with decent debt/equity, healthy margins, earnings growth.
- Exclude those with weak or deteriorating fundamentals.
This keeps you from chasing purely volatile “pump and dumps.”
Step 2: Sector & Market Context Analysis
Even good stocks can suffer if their sector is collapsing.
- Determine which sectors are favored or under pressure.
- Read macroeconomic indicators (interest rates, inflation, commodity prices, geopolitical risk).
- Favor sectors that have potential tailwinds in current market regime.
Step 3: Chart Pattern + Technical Setup Confirmation
For each candidate:
- Identify consolidation zones or bases.
- Check for breakouts (price breaking resistance) with volume.
- Confirm trend alignment (e.g. price above moving average, upward slope).
- Check volatility indicators (ATR expansion, Bollinger Band width).
- Possibly use momentum oscillators like RSI or MACD to avoid overbought extremes.
Step 4: Define Entry, Stop-Loss & Target
Before entering:
- Specify the precise entry price (or a range).
- Determine your stop-loss (the price at which you exit to limit losses).
- Set a target price or expected reward/risk ratio (for example, aiming for a 2:1 or 3:1 ratio).
- If volatility is extremely high, adjust your stops more conservatively (tighter), or reduce position size.
Step 5: Execute With Discipline & Monitor Actively
- Enter only when all your conditions are met (avoid ad hoc deviations).
- Monitor price, volume, and emerging news.
- If market conditions worsen, consider closing prematurely to preserve capital.
Step 6: Exit Strategy & Trailing Management
- Use trailing stops: as price moves favorably, adjust the stop upward.
- Partial exits: you could lock in some gains by exiting part of your position.
- Use technical signals (e.g., breakdown of support, reversal patterns) to exit.
Step 7: Post-Trade Analysis
After a trade (win or loss), analyze:
- What went right?
- What went wrong?
- Did you follow your rules or deviate?
- What can you improve next time?
Constant feedback is how you evolve into a better stock picker in volatile environments.
Specific Strategies for Volatile Markets (With Examples)
Here are several strategies and methods investors/traders use when volatility is high. Some are more advanced, so pick ones that suit your experience and risk tolerance.
Strategy 1: Breakout Trading from Consolidation
As mentioned, volatile markets often reward breakout moves. Stocks that move sideways (consolidate) and then break out often experience strong follow-through.
But caution: false breakouts in volatile times are more frequent, so always use stops around breakout levels.
Strategy 2: Volatility Contraction Pattern (VCP)
Originally popularized by some technical traders, the VCP is a setup where volatility “contracts” (range narrows) several times, and then a breakout occurs. The contraction shows consolidating pressure, and when price breaks, it often surges.
Strategy 3: Pair Trading / Market Neutral
In volatile markets, directional bets can be risky. A pairs trade involves going long one stock and short another correlated stock. When the spread reverses, you profit.
This strategy is more advanced but can reduce directional market risk.
Strategy 4: Option Strategies (for advanced users)
If you have access to and familiarity with options:
- Long Strangle: buy a call and a put with different strikes. You profit if the stock moves sharply either way.
- Volatility-based trades: use implied volatility to target overpriced or underpriced options.
- Iron condors, butterflies: when expecting limited movement, but this is more nuance and carries risk.
These are for more experienced traders and require careful risk management.
Strategy 5: Dollar-Cost Averaging / Incremental Accumulation
For longer-term investors:
- Use rupee-cost averaging (or dollar-cost averaging) – buying small amounts at multiple levels. This reduces the risk of entering at the wrong time.
- Average down only if you believe in the underlying business and fundamentals remain intact.
Strategy 6: Tactical Asset Allocation & Rotation
Rather than trying to pick individual winners all the time, you can dynamically shift allocations between equities, bonds, cash, sectors, or geographies depending on which area has better risk-return prospects.
This is more macro-level but helps mitigate risk when volatility surges.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls (and How to Avoid Them)
When volatility is high, many investors make avoidable errors. Recognizing them helps you steer clear.
Mistake 1: Chasing stocks that already moved strongly
When you see a big price surge, it’s tempting to join late. But often the momentum is exhausted. Wait for pullbacks or fresh patterns.
Mistake 2: Ignoring risk and position sizing
Because volatility magnifies swings, a small mistake without proper sizing can blow up your account.
Mistake 3: Letting emotions take over
Fear and greed dominate in volatile markets. A sudden drop may trigger panic selling. Stick to your rules and framework.
Mistake 4: Overtrading
High volatility leads to many signals. But not every signal is valid. Being overly active can erode profits (due to commissions, slippage).
Mistake 5: Failing to adapt
Markets change. A strategy that worked in one volatility regime may not work in another. Be flexible to adapt.
Mistake 6: Ignoring macro, news, or policy risk
Volatility is often driven by macro factors (interest rates, central bank decisions, geopolitical events). Blind stock picking without context is dangerous.
Example Case Walk-Through (Hypothetical)
Let’s run through a hypothetical example of how to pick winning stocks in a volatile market using the framework above.
Market Context: Suppose the technology sector is volatile but showing signs of recovery; earnings season is approaching.
Step 1 (Screening):
You filter for tech stocks with beta > 1.5, and fundamentals such as low debt, growing revenues, good margins.
You find TechCo: consistent profits, decent growth, manageable debt.
Step 2 (Sector check):
Tech sector momentum is improving (semiconductors, cloud, AI). Macro indicators suggest easing interest rates soon.
Step 3 (Technical confirmation):
- TechCo has had a 3-month consolidation between ₹150 and ₹180.
- Volume is gradually decreasing, Bollinger Bands narrowing → volatility contraction.
- A break above ₹180 with volume could trigger a move.
- Price is above its 50-day MA, trending upward.
Step 4 (Entry, stop, target):
- Entry: ₹182 (if breakout sustains).
- Stop-loss: ₹170 (just below consolidation).
- Target: ₹220 (2:1+ reward/risk).
Step 5 (Execution):
You enter once price closes above ₹182 with volume confirmation. Position size is limited to 3% of your total capital.
Step 6 (Managing and exiting):
- As price advances to ₹190, you trail stop to ₹180.
- Later, price hits ₹210; you raise stop further, possibly booking partial profits.
- If price reverses and hits stop, you exit.
Step 7 (Review):
- Did you follow your plan?
- How did volatility behave?
- What adjustments would you make next time?
This is how you practically apply the framework.
Challenges & Limitations to Acknowledge
While this blog provides a solid framework, it is important to note:
- No method yields guaranteed success — all investing involves risk.
- Volatility can change regimes quickly; what works now might not work tomorrow.
- Transaction costs, slippage, taxes, liquidity—all practical constraints.
- Emotional discipline is often the hardest part.
- Markets are influenced by unknown, unpredictable events (black swans).
Thus, approach stock picking as a continual learning process, not a static formula.
Summary & Final Thoughts
Volatile markets are challenging, but they also offer potential for outsized gains. If you follow a structured process, maintain your rules, and continuously learn from each trade, you stand a much better chance of success.






